This site
is mobile
responsive
The advent of multiple technology categories such as the Internet of Things (IoT), Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) are driving the wave of IR4.0. This is further accelerated by the arrival of the pandemic which has caused massive technological and economic shifts; reshaping the way modern society works. The 5G technology then becomes a unifying force to consolidate these different innovations as higher digital connectivity becomes critical in opening up opportunities for businesses and enterprises as well as countries to maintain economic growth and competitiveness.
Based on reports from IHS Markit, the 5G global value chain is expected to generate US$3.6 trillion in economic output and create 22.3 million jobs globally by 2035. With 5G deployment taking shape, consumer demand will be key for monetisation and continual expansion will be required to strengthen the 5G technology base. From 2020 to 2035, IHS Markit anticipates that the collective investment in R&D and CAPEX in the 5G global value chain will average over US$235 billion annually [1]. Notably, 5G has stimulated growth in the telecommunication market. Ericsson’s latest Mobility Report estimated that the number of 5G subscriptions will reach 1 billion globally by 2022.
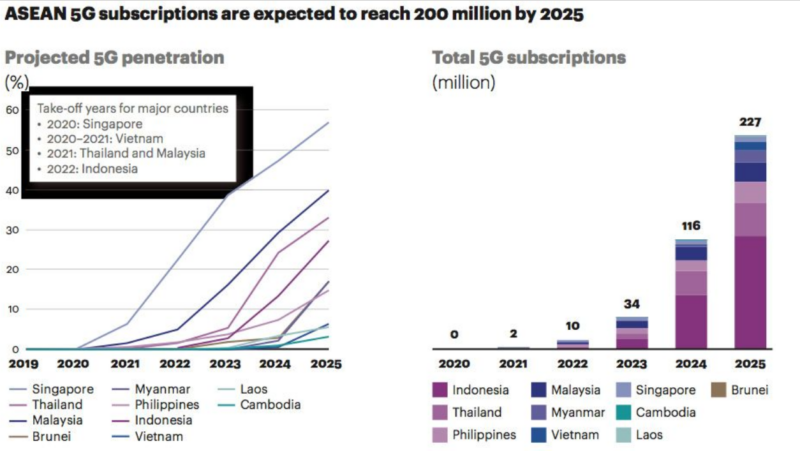
In the ASEAN region, 5G penetration is projected to cover 25 to 40 per cent by 2025 reaching a total of 200 million subscribers.
Malaysia is expected to achieve approximately 80 per cent of 5G network coverage in populated areas by the end of 2024, starting with a 10 per cent target of 5G coverage in Kuala Lumpur, Putrajaya and Cyberjaya by the end of this year. It is estimated that there will be approximately 2.1 million mobile 5G subscriptions in Malaysia by 2025, with an estimated penetration of 6.6 mobile 5G subscriptions per 100 people.

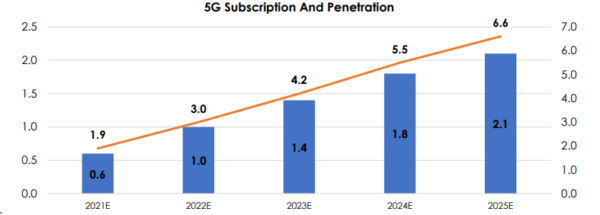
Projection of 5G Subscription and Penetration in Malaysia[3]
[3] National 5G Task Force Report, https://www.mcmc.gov.my/skmmgovmy/media/General/pdf/The-National-5G-Task-Force-Report.pdf
According to research conducted by the Malaysian Institute of Economic Research (MIER), 5G related economic activities are estimated to contribute an additional RM12.7 billion to the GDP between 2021 and 2025. In 2025 alone, the contribution of 5G to the Malaysian GDP is expected to reach RM5.3 billion in subsequent years, the share of 5G, and 5G-enabled Industry 4.0 activities in the Malaysian GDP is projected to continuously rise.
The demand for 5G will cut across numerous industries in the manufacturing sector, specifically among the semiconductor components and modules industry players, namely Outsourced Assembly and Test (OSAT) companies and Automatic Test Equipment (ATE) manufacturers. Companies such as Inari Amertron, Malaysian Pacific Industries (MPI) and Aemulus are set to be key beneficiaries, given their exposure to RF chips assembly, packaging and testing processes.
This technology also paves the way for smart manufacturing by enabling autonomous operations and remote management of production lines through the use of devices such as automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and vision quality checks involving cameras, computer vision, and machine learning.
While the benefits of 5G technology is far-reaching, the implementation of this technology’s potential is not without its challenges. Significant capital expenditure is required for the 5G rollout, particularly as it may involve semiconductor applications such as IoT, AR, VR and AI. Due to the dynamic complexity of the technology, it is also crucial to ensure that 5G networks meet the requirements which include latency and high throughput as well as to provide massive connectivity. Furthermore, the recent global semiconductor chip shortage has also impacted the supply chain of 5G enabled products that could hamper the growth of 5G in the market.
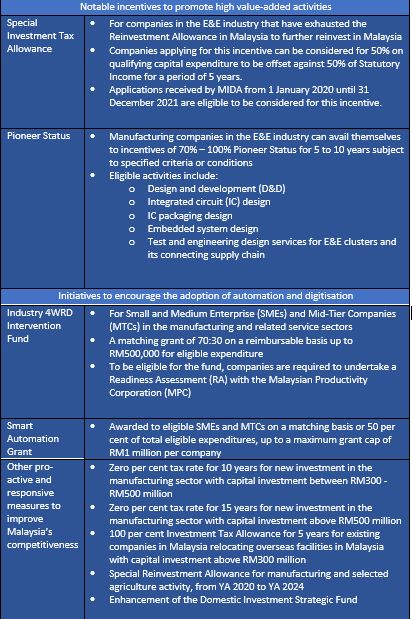
Notwithstanding these setbacks, the Malaysian Government remains committed to the roll-out of 5G, placing connectivity as one of the country’s priorities. In the coming years, the Government will be injecting RM11 billion to deploy the country’s 5G network over the next 10 years.
Under the National Digital Network Plan (JENDELA), specific action plans and targets will lay the foundation and prepare the country for the transition to the 5G technology. This comprehensive digital infrastructure plan aims to provide greater digital connectivity and address gaps in the digital divide in the country. The focus is on facilitating availability in terms of connectivity, recipient, regulation and industry, whereby 70 per cent of the 5G deployment will be for the use of industries while the remaining 30 per cent will be among the general public.
Various capacity building and innovation programmes will be held to support local vendor development and participation, as well as to boost 5G adoption among the public to develop use cases in accelerating industry participation. The 5G Demonstration Project showed success, such as in the oil and gas industry when robots were used to replace engineers remotely, as well as solving two major problems for the oil and gas industry especially on the rig, namely worker safety and increasing efficiency. The tourism sector also stands to benefit from the opportunities unlocked by 5G such as offering new tour experiences using VR technology, providing immersive 360- degree views of attractions through HD video live streaming, VR lenses or LCD panels.
Various engagements with associations and the business community are currently undertaken to highlight the relevant policies, government facilitation and Industry4WRD initiatives that are available. These include industry-focused seminars, dialogues with business chambers, briefings with business associations, industry workshops and supplier conferences to create awareness and encourage the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies.
Looking forward
5G will assume a critical role in the digital economy for the foreseeable future. Local companies must start exploring and be ready to capitalise on the opportunities of 5G once it becomes widely available nationwide. With more processes across various industries being automated or digitised, Malaysia has enormous potential to become the regional hub for advanced technology equipment and high-tech automation.
Given the Government’s strong desire to bridge the connectivity gap and its emphasis on leveraging 5G networks to achieve its Digital Economy aspirations, MIDA continues to work with service providers for Industry 4.0 and link them to manufacturing firms to help implement technologies, processes and skill development towards transitioning Malaysia into a fully indutrialised and advanced nation. This is in line with the National Investment Aspirations (NIA) to propel the country’s long-term growth through the flow of sustainable quality investments in new and complex growth, well beyond the curent COVID-19 situation.
For companies interested to explore the opportunities arising from the 5G technology, please contact the Electrical and Electronics Division of MIDA