
This site
is mobile
responsive

The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development’s (OECD) initiative to introduce 15 per cent Global Minimum Tax (GMT), though beneficial in addressing tax avoidance and competition issues, will influence investment decisions of multinational corporations (MNCs) and affect countries that are heavily reliant on tax incentives to attract inward investment.
Due to commence in 2023, the GMT implementation will change the way MNCs decide on investment destinations, especially given the large impact tax incentives have on investment considerations and business bottom lines. Moving forward, supporting factors such as ecosystem strengths and enablers should be given due emphasis as the primary magnets in attracting investments. Being the principal investment promotion agency of Malaysia, MIDA has long advocated the ecosystem approach to enhance the country’s competitiveness and sustainability.
By leveraging enablers like infrastructure and supporting industries through a cluster-based ecosystem approach, MIDA hopes to better address investors’ needs. In tandem with this, MIDA has continued to elevate industrial estates (IEs) in Malaysia as an important tool for attracting investment and technology, given that IEs often house several key factors that influence MNCs’ investment decisions: the availability of land, infrastructure, quality services and proximity to strategic markets.
The nation now houses more than 700 IEs, catering to a broad range of industries such as small-scale industries, heavy industries, halal as well as science and technology intensive activities. As some of these IEs were developed during the early years of industrialisation journey, the government continues to assume an active role in the maintenance and upgrading of infrastructures towards ensuring these IEs provide conducive environments for investors to operate.
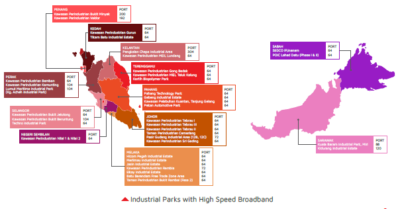
With the rise of the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR), MIDA has embarked on additional steps through the implementation of High-Speed Broadband (HSBB) across the country’s business premises. This initiative reflects MIDA’s commitment in providing seamless and stable connectivity to support 4IR undertakings by investors.
Launched in 2020, the HSBB programme is one of the action plans under the Technical Working Group – Digital infrastructure and Ecosystem (TWG-I) under the Industry4WRD: National Policy on Industry 4.0. The programme aims to strengthen digital connectivity in selected major IEs to facilitate the adoption of 4IR technologies by businesses in Malaysia.
The TWG-I, together with the Federation of Malaysian Manufacturers (FMM) and SME Association of Malaysia (SMEA), have identified 37 potential IEs across the country for the installation of HSBB digital infrastructure. In executing the programme, MIDA had collaborated with two of Malaysia’s top telecommunication operators: Telekom Malaysia Berhad (TM) and Maxis Broadband Sdn Bhd (Maxis).
Despite COVID-19 challenges, the deployment of HSBB accessibility services to all identified 37 IEs was successfully completed by 31 July 2021. As a result, companies in these IEs can enjoy seamless and stable high-speed internet connectivity of up to 1Gbps. Ultimately, MIDA is optimistic that this will provide impetus for more companies to adopt 4IR technologies, which is more crucial now than ever amidst the accelerated digitisation the pandemic has brought on, and beyond.
Aside from being aligned to the Industry4WRD agenda, the HSBB programme also augurs well with the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO)’s economic, social and environmental indicators for the development of competitive, inclusive and sustainable industrial parks.
In this context, IT connectivity and telecommunications have been identified as one of the key components under the economic pillar. Inclusive and sustainable industrial parks are innovative and integrated interventions, which can support a nation in accelerating its digital industrialisation and structural transformation. Beyond 2021, MIDA will double-up its efforts in building a cohesive industrial ecosystem and business-friendly environment to entice more investors into Malaysia.
These strategies include improving digital industrial ecosystems, domestic supply chains, future talent development, industry-academia collaboration in research and development and commercial and innovation (R&D&C&I), government delivery and efficiency, infrastructure (IT/connectivity) and digitalisation technology landscape (Industry 4.0).
Source: MIDA e-Newsletter January 2022