This site
is mobile
responsive

Why are specialty chemicals important to the industry? To further explore the realm of specialty chemicals, this article will guide you through understanding the industry’s significance, especially to Malaysia’s ecosystem. Specialty chemicals are typically produced through batch processes, as opposed to commodity chemicals that use larger and continuous processes. The coverage of specialty chemicals is vast across various industries such as electronics and semiconductors, cosmetics and personal care, pharmaceuticals and biotechnology, automotive, food and beverages, construction and building materials, and many more.
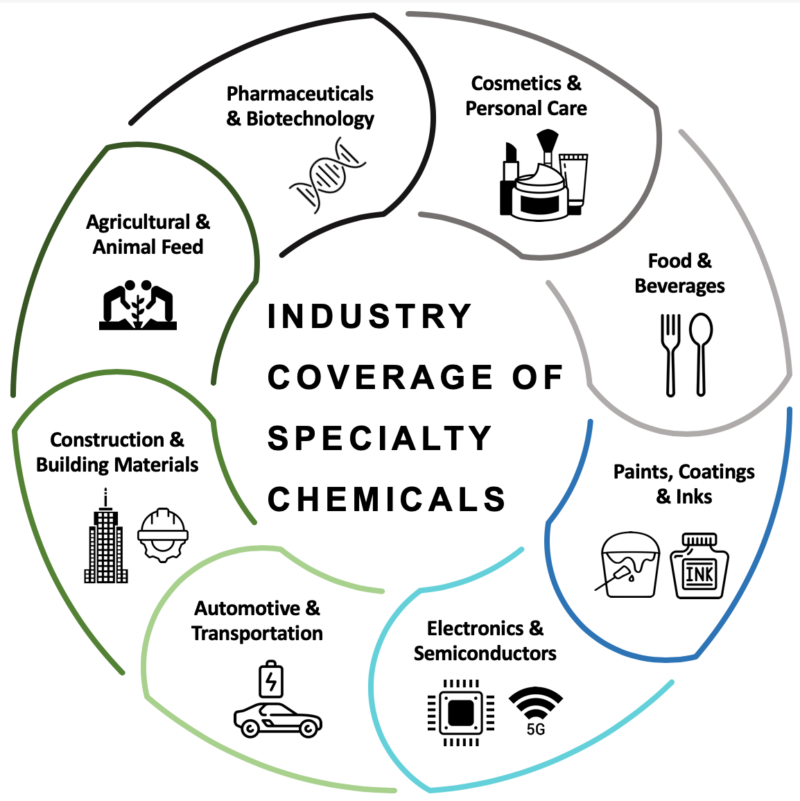
Figure 1: Usage of Specialty Chemical
Specialty chemicals have distinct characteristics that allow them to be used as modifying elements of chemical behaviours and performance in small quantities. Their unique molecular complexity gives them specific functions and a narrow range of applications. Some of the world’s leading manufacturers of specialty chemicals include large corporations such as BASF SE, Mitsubishi Chemical, Sumitomo Chemical, and DuPont.
Currently, a few specialty chemical producers exist in Malaysia but can scarcely cater to the needs of the electrical and electronics (E&E) industry. The E&E industry is ranked first among the top manufacturing industries in Malaysia for the year 2022. Amidst issues such as volatile energy prices, geopolitical tensions, global inflation, and major disruption of supply chains within the semiconductor industries, progressive trends and growth of technologies have led the E&E industry to be one of the rapidly growing sectors in the manufacturing industry. Major specialty electronic chemical players include Linde, Air Products, BASF SE, Cabot Microelectronics, and Solvay.
The demand for semiconductors is expected to drive the growth of specialty electronic chemicals by 5 per cent by 2026. As a result, the global market size for specialty electronic chemicals is estimated to be USD 1.61 billion in December 2022 with a CAGR of 8.5 per cent between 2022 to 2027. Asia Pacific has been identified as the largest region in the electronic chemicals market and is expected to be the fastest-growing region for the industry with rapid development of electronics and Electric Vehicle (EV) battery manufacturing sectors in countries such as India, China, and Japan.
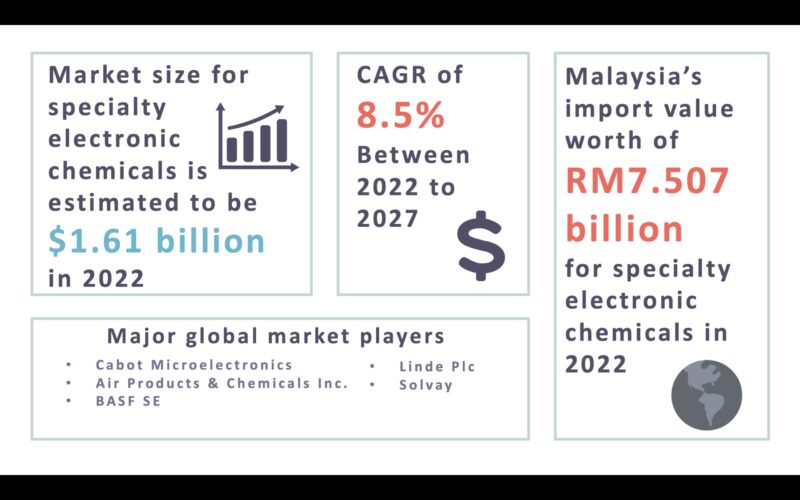
Figure 2: Specialty electronic chemicals information
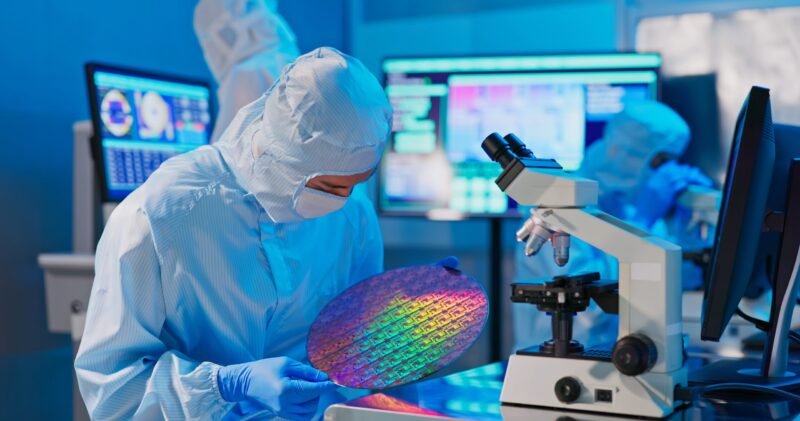
The usage of specialty electronic chemicals within the E&E is in processes such as doping, etching, cleaning, photolithography, and deposition. Chemical vapour deposition is one of the steps taken during wafer fabrication (front-end process) that creates a semiconducting material in which volatile precursors are introduced to alter its electrical properties. Here, wafer substrates (typically silicon) are exposed to doping gases (dopants) to produce semiconducting materials depending on their applications. Examples of dopants are rare gases such as arsenic (AsH3), diborane (B2H6), and phosphane (PH3). In addition, using epoxy as an adhesive such as polyimide or silicon-based materials is essential during the back-end process to secure manufactured chips to substrates or metal frames. Finally, hydrogen peroxide remains the most demanded specialty electronic chemical used during the front-end and back-end processes as it is often used during the etching and cleaning of integrated circuits (IC).
It has been identified that Malaysia’s E&E industry is are highly dependent on foreign supplies. As shown in Figure 4, the total importation of specialty electronic chemicals in Malaysia tremendously surged from 2019 to 2022. Here, the total import value of RM5.61 billion in 2021 increased to RM7.51 billion in 2022 which is 33.91 per cent from the value of its precedent year. Thus, by exploring the potential of manufacturing specialty electronic chemicals in Malaysia, the dependency of Malaysian supply on the foreign supply chain market can be reduced.
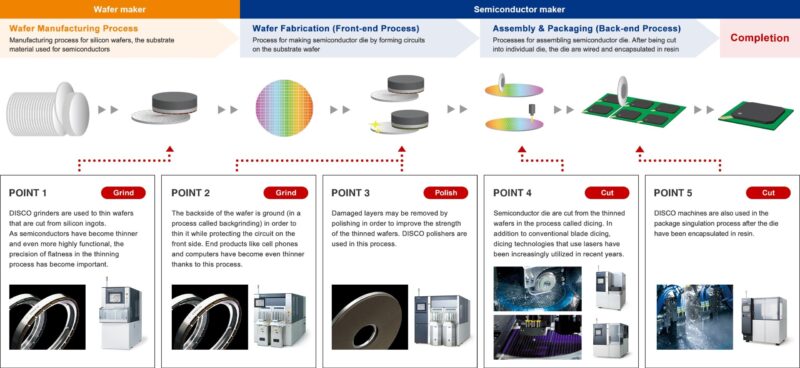
Figure 3: Semiconductor Manufacturing Process
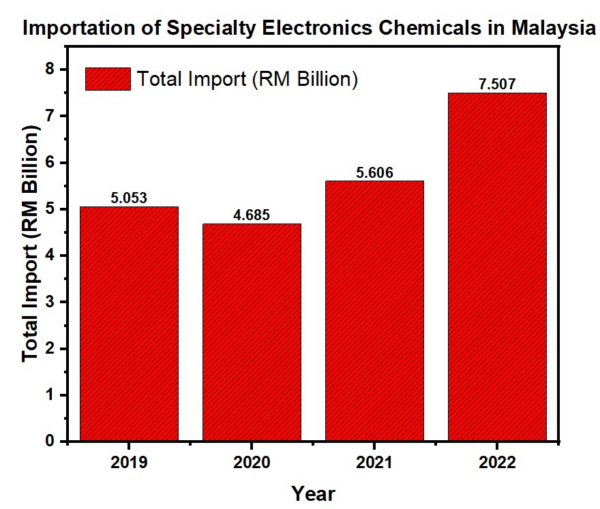
Figure 4: Malaysia’s import of specialty electronic chemicals data
MIDA as the government’s principal investment promotion and development agency, recognises the potential of specialty electronic chemicals in completing the gaps in our current E&E ecosystems. The promotion of this new growth area is vital as blueprinted in the National Investment Aspirations (NIA). With a holistic approach to ensure sustainable economic growth and strengthening Malaysia’s economic foundation, it is essential to keep track of major E&E market players and its sub-players within targeted pipelines to establish an integrated ecosystem. Understanding the need to develop a strong foundation to ensure Malaysia’s high-value economic growth and promoting product upscaling to qualify our local SMEs to be on par with major MNCs of E&E will be part of our initiative to elevate Malaysia’s economic development. Amongst the targeted specialty chemical supply chain to support our E&E industry is the existence of producers for chemicals such as etchants, dopants, adhesives, and photoresists.
Thus, to explore the prospect of this new growth area, interested investors may approach MIDA’s Chemical and Advanced Materials Division at https://www.mida.gov.my/staffdirectory/chemical-and-advanced-material/ for further assistance.