
This site
is mobile
responsive

Over the past years, the Malaysian electric vehicle (EV) industry has emerged as a beacon of innovation, reflecting the nation’s commitment to sustainable transportation and environmental conservation. Amid the ongoing global shift towards electrification in the automotive industry, Malaysia has strategically positioned itself as one of the significant participants in this whole green revolution.
According to Fortune Business Insights, the global EV market size is valued at USD388.1 billion as of 2023 and is expected to reach USD951.9 billion by 2030 with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 13.7 per cent.
Malaysia is well poised towards becoming a major producer of electric vehicles in Southeast Asia with the government’s proactive initiatives to foster a favourable EV ecosystem, supported by the presence of Tesla, which has a strong business commitment to the country’s automotive industry, solidifying Malaysia’s position at the forefront of the electric vehicle revolution in the region.
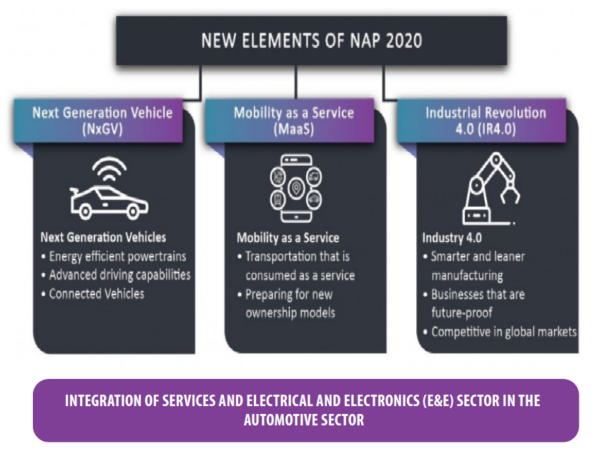
The National Automotive Policy (NAP) makes the development of the next-generation vehicle (NxGV) one of the main elements by focusing on three main strategies, namely value chain development, human capital development and safety, environment and consumerism.
The chemical industry assumes a crucial role in the EV revolution, driving innovations essential for the development, efficiency, and sustainability of EVs.
The cohesiveness of the chemical industry in the realm of sustainable EVs represents a sense of synergy between innovation, responsibility, and progress. As the world pivots towards more environmentally-friendly means of transport, the chemical sector has emerged as a central force, unifying diverse elements to propel the EV revolution towards unprecedented sustainability.

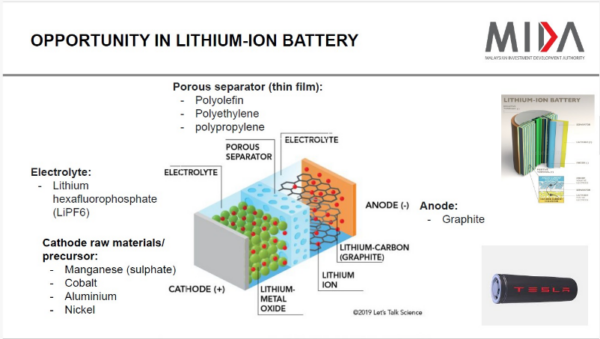
One of the major components in every electric vehicle is its battery, as the chemical industry provides breakthroughs for this important technology. Malaysian chemical companies are involved in the research and manufacturing advanced battery materials, including cathodes, anodes, and electrolytes. Their expertise enhances battery efficiency, charging speeds, and overall lifespan, ensuring that Malaysian-made EV batteries are competitive on the global stage.
Lithium is a key component of the batteries that are used in EVs and as renewable energy (RE) storage. Based on current projections, it is estimated that the world will need around 240 million tonnes of lithium by 2030. This is more than six times the estimated current global lithium reserves. This rapid increase in demand is driven by the growing popularity of EVs and other RE initiatives.
Through cutting-edge research and development, the chemical industry players have achieved remarkable progress in enhancing the energy density, charging speed, and overall performance of lithium-ion batteries, making them more efficient and suitable for a wide range of applications, including EVs.
Malaysia is actively advancing towards the production of lithium-ion batteries for the EV ecosystem, with notable players like Samsung SDI, EVE and APM Automotive. These promising projects have the potential to attract significant EV-related investments into Malaysia, thereby fostering the growth of a robust and healthy EV ecosystem in the country.
The mission to establish a robust EV ecosystem in Malaysia gains further momentum with the presence of INV New Material Technology, a company under Shenzhen Senior Technology Material – one of the leading enterprises in lithium battery separator technology in China. INV is poised to assume a vital role in EVs, electrical and electronics and solar energy through advances in separator technology. INV’s lithium-ion battery separator facility aligns seamlessly with Malaysia’s commitment to a sustainable future, reflecting responsible business practices. This marks Malaysia as one of the largest lithium-ion battery separator producers in Southeast Asia.
The development of advanced cathode materials such as lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) or lithium nickel cobalt manganese oxide (NCM) through precise chemical formulations are also making headways. These materials significantly influence the energy density, voltage, and thermal stability of lithium-ion batteries. Tailoring the chemical composition of cathodes can lead to batteries with higher capacities and longer lifespans.
Graphite, silicon, and other carbon-based materials are essential components of the anode in lithium-ion batteries. Chemical treatments and coatings can enhance the conductivity and structural integrity of anodes, enabling faster charging and discharging rates. Innovations in anode materials are vital for improving the overall performance and efficiency of lithium-ion batteries in EVs.
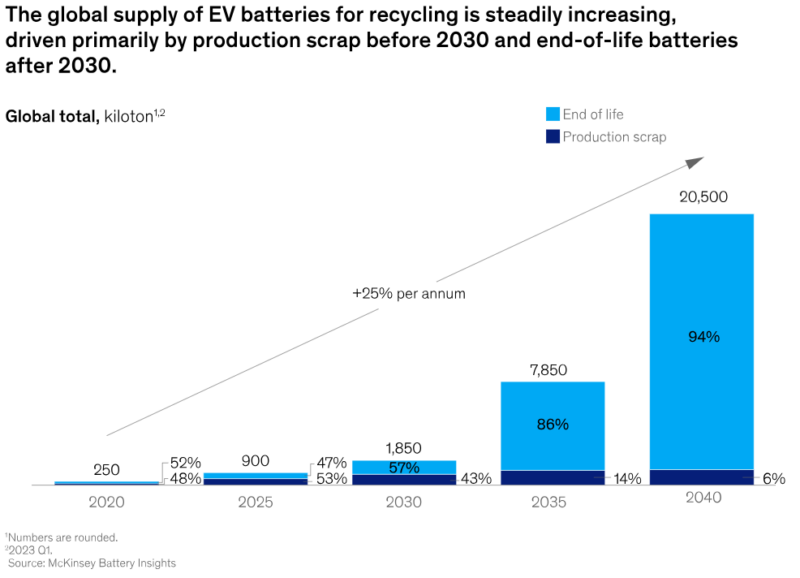
In China, Europe, and the United States, where substantial transitions to EVs are underway, the primary source of recyclable battery materials still stems largely from consumer electronics cells found in items like laptops and household devices. Additionally, a considerable portion comes from cell manufacturing scrap, typically originating from faulty batteries that do not meet quality control standards. It is important to acknowledge that manufacturing scrap will constitute a notable component when a new battery factory commences operations, creating a substantial volume available for recycling. This trend becomes increasingly significant in markets experiencing a surge in EV battery manufacturing.
End-of-life EV batteries constitute a significant volume in markets like China, where EV adoption has been widespread for a considerable period. However, on a global scale, production scrap is expected to continue being the main source of battery materials for recycling until 2030. It is projected that by that time, the volume of end-of-life EV batteries will have expanded to the extent of surpassing production scrap in terms of recycling potential.
Creating a sustainable battery industry for EVs necessitates a comprehensive approach spanning various aspects of production, usage, and disposal. One critical avenue is efficient battery recycling and reuse infrastructure, enabling the recovery of valuable materials and promoting a circular economy. By establishing widespread recycling facilities and incentivising proper disposal, the industry can significantly reduce its environmental footprint. Material innovation assumes a pivotal role, focusing on reducing dependence on rare and environmentally sensitive elements such as cobalt while exploring sustainable alternatives. Additionally, promoting responsibly sourced materials, especially lithium, from ethical mining practices contributes to sustainable material sourcing.
Malaysia is currently in the early stages of lithium-ion battery production. Despite this, the country is making significant progress through comprehensive supply chain integration efforts. These efforts involve various steps such as manufacturing battery cells and assembling battery packs and promoting more industry players in the supply chain ecosystem. With these initiatives, Malaysia is on track to becoming a key player in the EV battery manufacturing industry.
In line with the Malaysian Government’s vision of heading towards a sustainable future by reducing its carbon footprints as well as elevating the EV industry, various forms of incentives and grant packages are available to promote the invention of robust batteries as well as a circular economy involved throughout the ecosystem.
MIDA, as the Government’s principal investment promotion and development agency, recognises the potential development of batteries in completing the ecosystem of the EV industry in Malaysia. Thus, we encourage investors to explore further the business prospects of this new growth area by engaging with the dedicated team at the Chemical and Advanced Material Division at https://www.mida.gov.my/staffdirectory/chemical-and-advanced-material/.
