This site
is mobile
responsive

Malaysia has an open economy which is driven by trade in goods and services. Over the years, the country has forged an extensive network of implemented regional and bilateral trade agreements which have enabled Malaysia-based exporters and investors to enjoy a myriad of benefits such as tariff concessions, expanded market access, and strengthened economic integration with partner nations and regions. As a result, Malaysia’s robust international trade activities have played a key role in driving its sustained economic growth and overall development, firmly establishing the nation as a prominent player in the global marketplace.
Malaysia highly values international trade and investment as a key driver of its economic growth. To this end, the country has ratified seven bilateral Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) with Australia, Chile, India, Japan, New Zealand, Pakistan and Turkiye.
Additionally, Malaysia and its ASEAN partners are parties to several trade agreements, including the ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA), ASEAN-Japan Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (AJCEP), ASEAN Korea Free Trade Agreement (AKFTA), ASEAN-China Free Trade Agreement (ACFTA), ASEAN-Australia-New Zealand Free Trade Agreement (AANZFTA), ASEAN-India Free Trade Agreement (AIFTA) and ASEAN-Hong Kong Free Trade Agreement (AHKFTA).

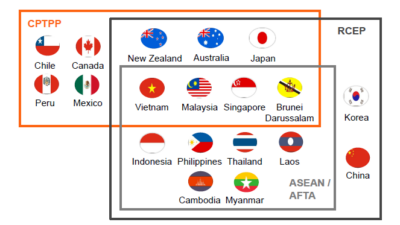
The year 2022 marked significant milestones for Malaysia’s trade relationships with the ratification of two mega free trade agreements.
Both RCEP and CPTPP aim to create a favourable investment environment in the region. The RCEP focuses on promoting, facilitating, protecting, and liberalising investments as well as fostering a pro-business and competitive investment landscape. The agreement also introduces enhanced investment facilitation provisions and investor aftercare. In its entirety, this collective effort contributes to the growth and advancement of local industries while simultaneously attracting foreign investment.
A common feature of many FTAs is the inclusion of a chapter on Economics and Cooperation, which is designed to address development gaps and maximise mutual benefits among participating countries. This chapter places a strong emphasis on capacity-building and technical assistance initiatives among the FTA parties. By prioritising these measures, FTAs promote the exchange of knowledge, expertise, and resources, enabling countries to enhance their economic capabilities and bridge developmental disparities.
The Malaysian government recognises the importance of FTAs as mechanisms to facilitate market access for Malaysian businesses, aligning with the country’s strategy to integrate further into global value chains and diversify its economy. To complement the use of FTAs and strengthen Malaysia’s investment and trade ecosystems, the government has implemented various policies, including:
Taken together, the span, depth and innovative elements of Malaysia’s trade agreements hold much promise for businesses, and opportunities for its people. Ministries and Agencies have implemented a range of initiatives to enhance the capacity and capabilities of Malaysian businesses, particularly small and medium enterprises (SMEs). It is essential that companies fully understand and benefit from the full suite of these trade agreements. These initiatives empower SMEs to achieve economies of scale, expand market share, and increase productivity. By strengthening their capabilities, Malaysia nurtures a competitive business ecosystem that effectively harnesses the benefits derived from FTAs and global trade integration, driving economic growth and opening doors for new opportunities.