This site
is mobile
responsive
Business Ready Environment
Starting and expanding your business in Malaysia is a straightforward process. Malaysia’s robust financial and banking sectors, pro-business policies, well-developed infrastructure, and government support makes it easy to do business here.
Perfectly positioned as a central hub for worldwide trade routes, Malaysia offers a top-tier air transport infrastructure. Complemented by our strategic coastal ports, which serve as an accessible maritime link vital for global commerce, Malaysia facilitates seamless business operations and enhances investment prospects across continents. Additionally, Malaysia provides a selection of secure trade corridors and industrial zones, enabling uninterrupted supply chains and business activities.
Malaysia maintains pro-business policies that are both sensible and practical, fostering a secure and conducive environment for your business to prosper. These policies encompass flexible incentives, strong intellectual property protection laws in line with global standards, and the freedom to have 100% equity ownership in manufacturing and select service sectors.
Our efforts in attracting investments and driving productivity and innovation through economic and regulatory reforms have received worldwide recognition by various international institutions.
Malaysia is committed to continuously developing and upgrading its infrastructure. This has resulted in over 500 dedicated industrial parks, specialised industrial parks and free industrial zones, expanding telecommunication technologies, growing network of highways, efficient seaports and well-recognised international airports.
500+
Malaysia has over 500
industrial parks
22
Malaysia has 22
Free Industrial Zones (FIZS)
Malaysia’s top-tier infrastructure and business-friendly environment make it an attractive destination for investors across various industries. The country boasts over 500 industrial parks catering to sectors such as small-scale industries, halal products, biotechnology, eco-parks, and high-tech industries. These parks are designed to offer essential amenities, including easy access to major towns, reliable electricity and water, high-speed broadband up to 1Gbps, gas pipelines, storage facilities, and robust security. Ready-built facilities and ‘plug and play’ zones reduce start-up costs, making it easier for companies to quickly begin operations. Additionally, companies located in Free Industrial Zones (FIZs) benefit from duty-free imports of raw materials, components, parts, machinery, and equipment required for manufacturing. In areas without FIZs, companies can apply to establish Licensed Manufacturing Warehouses (LMWs) to enjoy similar advantages.
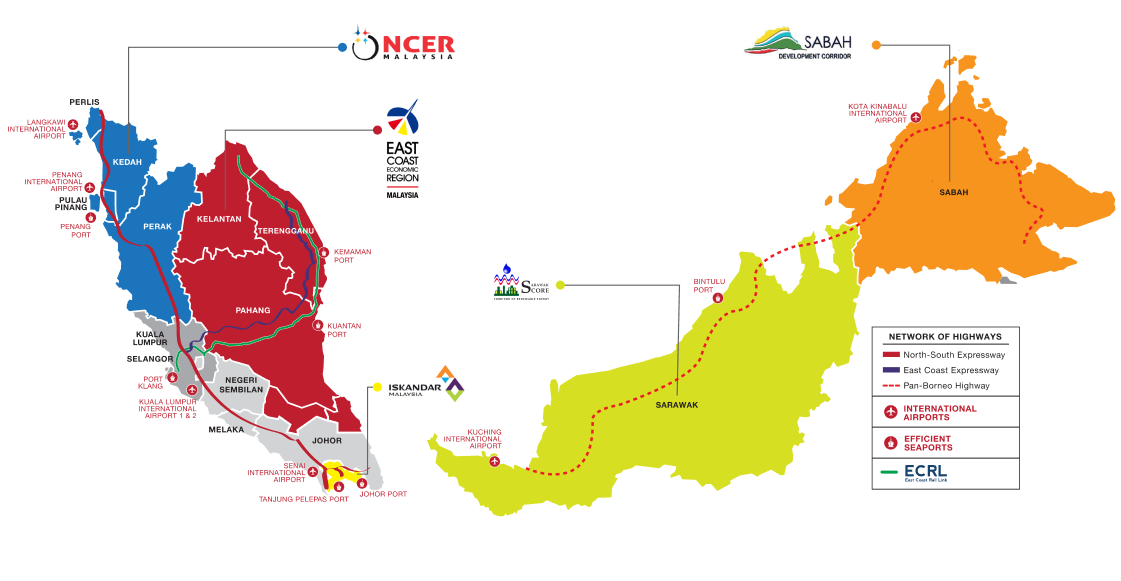
Complementing this infrastructure are Malaysia’s five key economic regions, which play a vital role in driving regional growth and socio-economic progress. The Northern Corridor Economic Region (NCER), covering Perlis, Kedah, Pulau Pinang, and Perak, focuses on high-value-added projects to encourage private investment. The East Coast Economic Region (ECER), spanning Kelantan, Terengganu, Pahang, and parts of Johor, promotes human capital development and works to bridge the rural-urban divide. In the south, Iskandar Malaysia acts as a flagship initiative to attract investment and boost growth in Johor. The Sarawak Corridor of Renewable Energy (SCORE) promotes sustainable development in central Sarawak through renewable energy initiatives, while the Sabah Development Corridor (SDC) supports economic upliftment in Sabah. Together, these regions, supported by excellent infrastructure and strategic incentives, form a dynamic network that drives Malaysia’s overall growth and competitiveness.
Malaysia’s liberal equity policy enables your businesses to establish a strong presence and gain a competitive edge. Since June 2003, foreign investors have been allowed 100% equity ownership in new, expansion, and diversification projects within the manufacturing sector and specific services sector. The liberalised services sub-sectors encompass health and social services, tourism services, transport services, business services, and computer-related services.
Malaysia’s IP laws are in conformance with international standards
Malaysia has signed Investment Guarantee Agreements (IGAs) with more than 60 countries.
Our robust Intellectual Property (IP) protection attracts the world’s most innovative companies. Our secure IP laws safeguard not only ideas and concepts but also vital business assets crucial to long-term success.
To illustrate, Intel, through its Malaysian Global Service Centre, generates value for its customers and stakeholders. The centre conducts R&D for computing devices and offers diverse services including finance, human resources, information technology, procurement, manufacturing, logistics, warehousing, and sales marketing support.
With over RM14 billion invested over the span of 50 years and employing over 9,000 highly skilled Malaysians, Intel’s first offshore assembly plant established in 1972 has now become the largest assembly and test site in its global network, located here in Penang.

Design

Patents

Invention

Authorship
Law

Copyright

Protection

Brand
The US Chamber of Commerce’s Global Innovation Policy Centre (GIPC), in its 7th Annual International Intellectual Property (IP) index – 2022, ranks Malaysia second in South-East Asia.
Malaysia actively fosters a dynamic R&D environment with incentives for IP development, meeting the demand for global innovation amid evolving technologies and businesses.
Malaysia’s conducive environment positions it as a leading global destination for manufacturing. With over 5,000 foreign companies from more than 50 countries establishing their presence, it reflects unwavering confidence in Malaysia as the preferred destination for your global growth investment.
Malaysia attracts a hybrid suite of business models, which include Global/Regional Headquarters, Centres of Excellence (COEs), Procurement and Distribution Hubs, offering numerous advantages to multinational corporations (MNCs) looking for a strategic hub in the Asia-Pacific region to efficiently manage their service operations and regional or global supply chains.
The NIA serves as a visionary growth framework to drive extensive reforms in Malaysia’s investment policies. It focuses on coherence and is reflected across all national policy papers and initiatives related to investment, including the New Industrial Master Plan and the 12th Malaysia Plan. This framework assumes an important role in revitalising Malaysia’s investment environment to attract high quality investments and create high-income employment opportunities.

Increase the Economic Complexity
Enabling comprehensive reform in strengthening economic diversity and complexity of exports, enhanced local Research and Development (R&D), an improved capabilities, for a broader array of high-value products and services.

Create High-Value Jobs
Create high skill jobs to provide better income for the people.

Extend Domestic Linkages
Expanding and integrating domestic linkages into regional and global supply chains by improving resiliency.

Develop New and Existing Clusters
Accelerating the formation of new clusters in high-growth sectors while developing existing clusters to boost productivity, value creation, and economic effect.

Improve Inclusivity
Promoting inclusive growth focusing on socio-economic development.
The NIA aims to drive sustainable and high-quality investment in emerging and diverse sectors, fuelling Malaysia’s long-term growth. MIDA, with its established track record in promoting and facilitating investments, will assume a vital role in this initiative aligning with institutional reforms and the NIA’s mandate for improved policy coherence.
Under the NIA, investment strategies will prioritise investments and innovation that strike a balance between economic and environmental sustainability anchored on global environmental, social and governance (ESG) benchmarks to support growth along the supply and value chains.
The green initiatives under Budget 2022 include reinforcing the need for Malaysian companies and the local supply chain to adopt ESG frameworks premised on higher value creation.
The transforming strategic sectors that have been identified following ESG-based practices include:
The 12MP encompasses Economic Empowerment, Environmental Sustainability, and Social Reengineering, working in harmony for Malaysia’s vision of Shared Prosperity. These dimensions align with Malaysia’s commitment to the Sustainable Development Goals by 2030. For more details, visit the Official Portal of the Ministry of Economy.